
Italian Modal Verbs And How To Use Them
The modal verbs are: dovere (to have to, must), potere (to be able to, can), and volere (to want to, would). Italian modal verbs have some similarities with English modal verbs, because they are used together with verbs in the infinitive, but there are differences, too. In English, for example, we can use "to be able to," which does get.

Italian modal verbs Learning italian, Italian language, Italian words
Modal verbs tend to be in company with the base form of the verb meaning the action, while the modal verb signifies its modality: whether we are referring to ability, likelihood, request, permission, suggestion, obligation, etc. All Italian modal verbs have irregular present forms, and at least two of them tend to be very confusing for English.

Your Italian Tutor Italian modal verbs
Italian modal verbs. First of all, an Italian verb can be defined as "modal" or "servile" when it has the function of specifying the relationship between the subject and the verb that follows it. Italian modal verbs are: DOVERE - POTERE - VOLERE. Before moving on to the examples of the Italian modal verbs with the English ones, let.

ITALIAN VERBS LIST 1 Teaching Resources Italian verbs, Teaching
This modal verbs can be used alone or with an infinitive verb right after. "Voglio bere un caffè" : you are stressing the fact that you really really want to drink a coffee. It's a strong desire for you. Both sentences are correct and both make it clear what you want to do. If you use VOLERE + an infinite you are stressing more your desire.

italian verb endings Bing Italian verbs, Italian lessons, Verb
Modal Verbs in Italian. The three modal verbs are: potere - can, be able to, may. volere - to want, to want to. dovere - must, have to, owe. All three modal verbs have irregularities so you will need to learn them individually, but once you do, you'll be able to form all sorts of sentences on your own!

Modal Verbs Italian The Italian Present Conditional Commonly Used
Italian modal verbs are followed by an infinitive verb. That's it, that's what sets them apart from the other verbs. The infinitive verb is a verb in its basic form, the one you look up in a dizionario, dictionary. This means that any verb after potere, volere, dovere and sapere must NOT be conjugated. You only need to conjugate the modal verb.

The Top 4 Italian Modal Verbs in 2023 Learning italian, Italian
Mastering Italian modal verbs is crucial for expressing various nuances and shades of meaning in the language. By understanding the conjugation and usage of volere, potere, and dovere, you will significantly enhance your Italian communication skills. Practice using these verbs in different contexts to become more fluent and confident in your.

Modal Verbs of Ability Modal verbs, English language teaching, Parts
The Italian modal verbs dovere, potere, and volere express necessity, possibility, and desire, respectively. They are also used to request permission, make requests, and offer assistance. Modal verbs are always followed by an infinitive and are irregular, so they need to be memorized. Since they are high-frequency verbs, it's crucial to know.

Italian Verbs Ilazed Ilaria Ziccardi
The Italian modal verbs are dovere, potere, volere—meaning, respectively: "necessity," "possibility," and "volition"—they precede the infinitive of another verb and indicate a mode, such as in the following examples. The sentences show how to use these three verbs in Italian, followed by the type of mode in parentheses, followed by the.

Modal Verbs in Italian YouTube
The helping or modal verbs, volere (to want), dovere (to have to), and potere (to be able to), appropriately called in Italian verbi servili, or servile verbs, enable the expression of the action of other verbs in the light of our wish, intention, or determination; duty, necessity, or obligation; possibility, ability, or power. I want to dance.

Feeling Tense? Italian Modal Verbs Free Basic Italian
The Italian modal verbs (verbi modali) are used to express the specific modality of an action. Structure of clauses with modal verbs: The modal verbs are used with the infinitive form of the specific verb that specify the particular action. -Subject + modal verb + infinitive ExampleTranslation-Io devo spedire questa e-mail entro stasera. -I must send this e-mail before this evening.

The Italian Modal Verbs Explained for Beginners Italian verbs, How to
Modal verbs in Italian are very simple. Let's learn the three modal verbs potere, dovere and volere in Italian. Modal verbs in Italian. The modal verbs are irregular. The conjugation follows: POTERE can, be allowed: DOVERE must, have to: VOLERE want: io: posso: devo: voglio: tu: puoi: devi: vuoi:
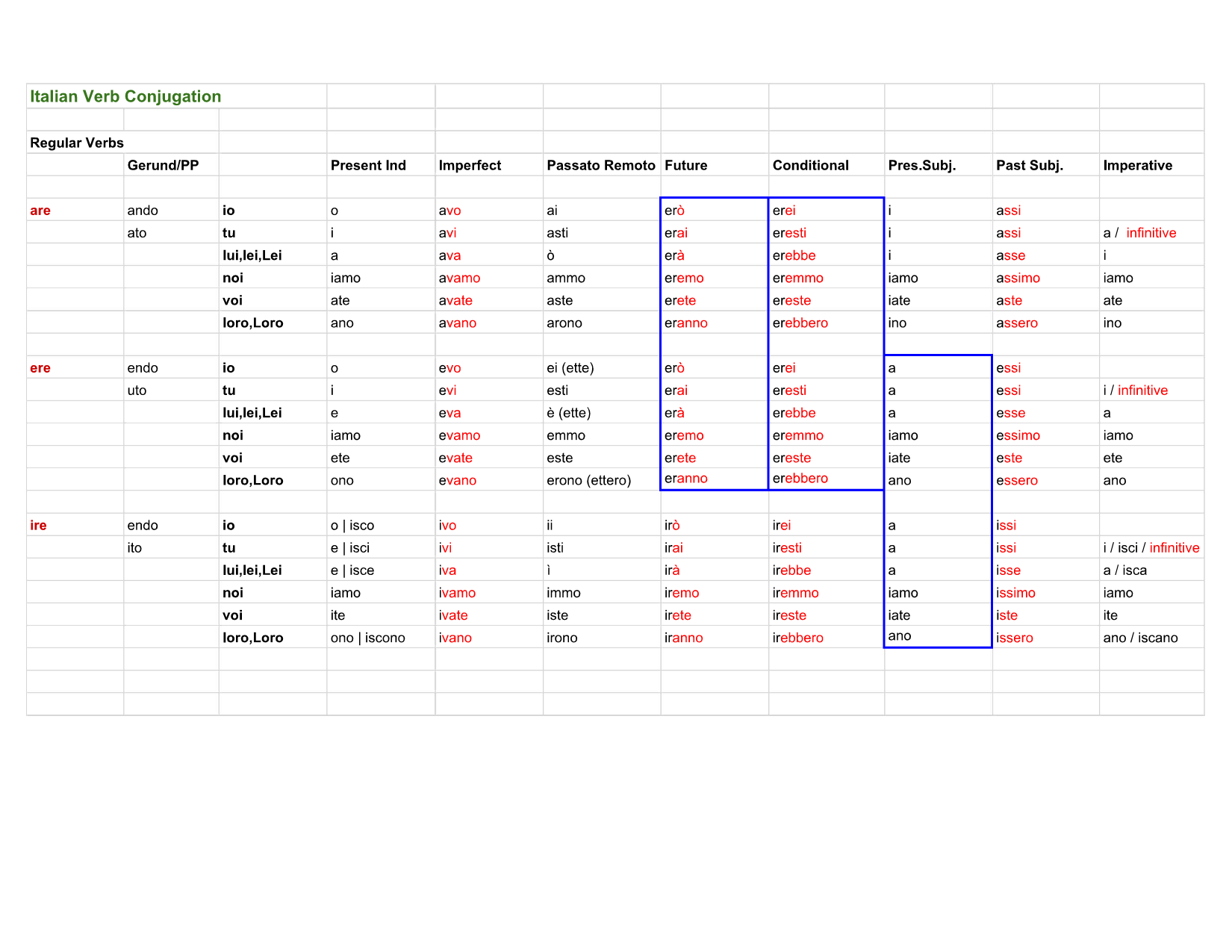
Italian Regular Verbs Arnold Solof
In English, some of the most common modal verbs include can, could, may, might, shall, should, will, would, and must whereas in Italian, there are just four to worry about: Volere. to want. Potere. to can / to be able to. Dovere. to have to / to must. Sapere. to know how to / to be able to.

Top 24 Most Important Verbs in Italian (Plus PDF CheatSheet & Quiz) (2022)
The four modal verbs in Italian are: Dovere (means 'must', expresses necessity) Potere (means 'can', expresses possibility) Volere (means 'to want', expresses intent) Sapere (means 'to know' but when used as a modal verb it mostly means 'can', expresses ability) Let's have a closer look at each of these four modal verbs!

Italian modal verbs doverepoterevolere Italian with Prof Corsini
Understanding Italian Modal Verbs Posted by Geoff on Aug 1, 2017 in Grammar. Volere (to want), dovere (to have to) and potere (to be able to) are the three so called modal verbs. As verbs go, they are not particularly difficult to conjugate. until you need to use them in the present perfect (passato prossimo).

Learn Italian Modal Verbs Will, Power, Duty, Know Story Telling Co
There are certain verbs in Italian that are called modal verbs, because they serve the verb that follows them. These verbs are dovere, volere, and potere, wh.